Bloomberg News/Landov
Bloomberg News/Landov
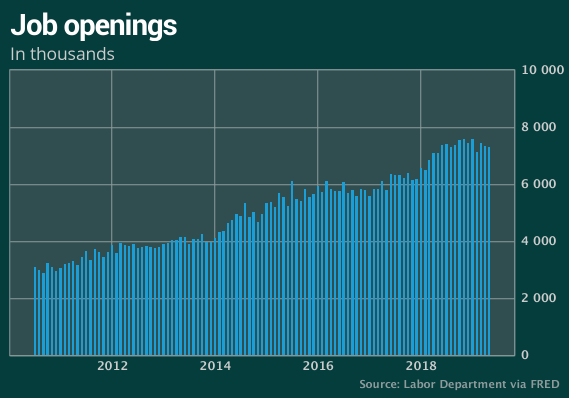
The numbers: Job openings in the U.S. fell to slightly to 7.32 million in May, but they remained near a record high and suggest that hiring is unlikely to slow dramatically even though the economy has softened.
Companies hired 5.73 million people in May, down from 6 million in the prior month. Yet separations — people who quit, retire, die or get laid off — fell by a similar amount.
The decline hiring in May doesn’t come as a shock. The U.S. only added 72,000 new jobs that month, according to the government’s monthly employment tally.
Hiring has waned in manufacturing and other export-heavy industries owing to ongoing trade tensions and a weaker global economy. The much larger service side of the economy is still adding plenty of new jobs, however, as reflected by a snapback in hiring in June.
Read: Job creation rebounds, calming worries about the economy
What happened: Openings rose in manufacturing, education, professional occupations and hotels and restaurants, the Labor Department said Tuesday.
Fewer job listings were posted in construction, transportation, government and media.
For the 15th straight month, job openings outnumbered the unemployed. There were 1.3 million more job listed jobs compared to 6 million people officially classified by the government as unemployed.
The share of people who left jobs on their own, known as the quits rate, slipped to 2.5% from a postrecession peak of 2.6% among private-sector employees.
The rate for all workers, including government employees, stood at 2.3% for the 12th month in a row.
More people quitting is seen as a good sign because it means workers feel secure enough to leave one job for another. Typically workers who move also end up getting better pay.
Read: Weak unions, globalization not to blame for shrinking slice of income pie for workers
Big picture: Although job openings remain close to a postrecession high, companies have been more selective in their hiring. Many firms complain they can’t find enough skilled workers, and in some cases they’ve resorted to more automation.
Read: Robots are coming for your jobs — Oregon, Louisiana, Texas have most to lose
Slower economic growth and uncertainty about the outcome of trade talks with China also appear to have put a damper on hiring. The U.S. has added an average of 172,000 new jobs a month this year, compared to 223,000 in 2018.
The strongest labor market in decades, however, is likely to extend a record U.S. economic expansion at least through the end of the year.
Read: The U.S. economy just entered a record-shattering 11th year of expansion
The Dow Jones The Dow Jones Industrial Average DJIA, -0.32% and S&P 500 index SPX, -0.10% fell in Tuesday trades for the second day in a row. Stocks surged to record highs last week on relaxed trade tensions with China and on hopes the Federal Reserve would cut interest rates.
The 10-year Treasury yield TMUBMUSD10Y, +0.59% rose slightly to 2.06%. The yield has sunk from a seven-year high of 3.23% last October.