At some point over the next century, the stock market will lose more than 20% of its value in a single day. Maybe this doesn’t seem like useful advice, but the fact is that you’re kidding yourself if you think market crashes of such magnitude won’t happen again.
This sobering thought coincides with the 33rd anniversary of the 1987 U.S. stock market crash. On Oct. 19, 1987 — Black Monday — the Dow Jones Industrial Average DJIA, -0.31% lost 22.6%. It was the worst one-day percentage drop in U.S. stock market history. If a similarly-sized crash were to occur today, it would take about 6,500 points off the Dow in just one trading day.
Many regulatory reforms were instituted in the wake of the 1987 crash (as well as following other big subsequent drops, such as the so-called Flash Crash in May 2010). As a result, many investors have comforted themselves that another crash won’t happen.
That’s false comfort, according to research conducted by Xavier Gabaix, an economics professor at Harvard University. Two decades ago, along with three physicists at Boston College, he derived a formula that predicts the frequency of big daily changes over long periods of time. Though that frequency is low, it isn’t zero.
Read: This is the last chart investors need to see ahead of the ‘Black Monday’ market crash anniversary
Gabaix and his fellow researchers presented their research in December 2002 in the scientific journal Nature. To appreciate the model’s forecasting ability, consider that from that date until now — a period of 17.8 years — the formula would have predicted that there would be three days in which the market rose or fell by at least 10%. How many such days has the S&P 500 SPX, -0.42% experienced since December 2002? Three.
This casts a different light on the huge volatility the stock market experienced in March 2020 as the stock market reacted to the COVID-19 pandemic — including the S&P 500’s 12% plunge last March 16. People’s natural reaction at the time was to focus on the historically unique and idiosyncratic causes of that crash. While understandable, this reaction also overlooked the reality that a drop of such magnitude was inevitable, sooner or later.
Since a 17.8-year period is not long enough to illustrate the predicted frequency of plunges as big as the 1987 Crash, the chart below focuses on the past century. Notice that the researchers’ model does an impressively good job of matching what actually happened.
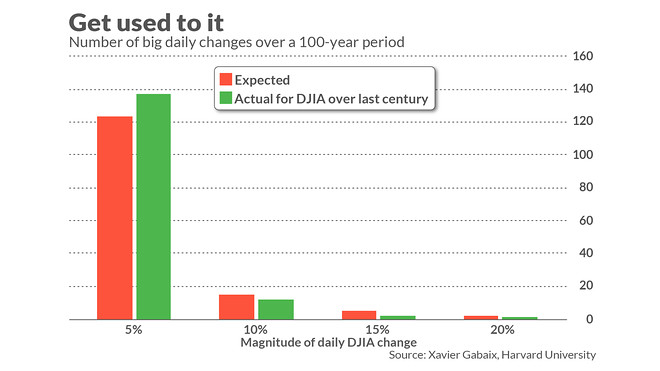
To be sure, the researchers’ model doesn’t predict when these big daily market changes will take place. It instead specifies their frequency over long periods. So it’s entirely possible that Wall Street could go for decades without experiencing another crash like 1987’s, or suffer another one in the next year. The point of the model is that, when it does happen, we shouldn’t be surprised.
There’s a loose analogy here with pandemics. Scientists have been predicting for years that a pandemic was not a matter of if, but when. Yet, since the odds of a pandemic in any given year were so small, it was hard to get many people interested in planning for how to react when the inevitable came to pass. In retrospect, it’s clear that we all would have been well served by better planning.
The same goes for investing. It’s been more than 30 years since the 1987 Crash. People who belong to generations Y and Z were either not born at that time or not old enough to have any real memories of it. Most Gen Xers were not even out of college. No wonder it’s difficult to get most of us to spend much time imagining how we might arrange our portfolios to survive another crash.
In other words, today’s market is dominated by investors who are too young to remember the 1987 crash. I’m reminded of what Adam Smith, the pseudonymous author of the late 1960s classic book “The Money Game,” called a “kids’ market.” He used that phrase to refer to speculative bull markets in which the advisers and traders making the most money are those too young to remember prior crashes. “Memory can get in the way of such a jolly market,” Smith wrote.
Smith described a friend of his on Wall Street called “The Great Winfield,” who exploited kids’ markets by only hiring investment managers who were not yet 30 years of age: “The strength of my kids is that they are too young to remember anything bad, and they are making so much money that they feel invincible. Now you know and I know that one day the orchestra will stop playing and the wind will rattle through the broken window panes, and the anticipation of this freezes [the rest of] us” who are old enough to remember.”
You might object to this analogy on the grounds that the stock market in March suffered its worst waterfall decline in U.S. history. Surely those memories are still fresh? But that decline is not what Winfield had in mind, since the stock market so quickly recovered. Today’s “kid” investors have filed away their memories of what happened in March under the category of “brief pause in the market’s inexorable march to new highs.” That’s hardly the kind of memory the anticipation of which “freezes” us.
Contrast this year with what happened between January 1973 and January 1985. At the end of that 12-year period, according to data from Yale University finance professor (and Nobel laureate) Robert Shiller, the stock market was no higher than where it was at the beginning on a dividend-adjusted and inflation-adjusted basis. Investors who lived through that dozen-year period were so traumatized that many swore of equities for the rest of their lives. The 1987 stock market crash had a similarly traumatic effect.
So if you are old enough to remember the 1987 Crash, memory will serve you well as you judge what kind of risk is appropriate. If you aren’t old enough, then you need to pay especially close attention to the academic studies which conclude that another crash is someday inevitable.
Mark Hulbert is a regular contributor to MarketWatch. His Hulbert Ratings tracks investment newsletters that pay a flat fee to be audited. He can be reached at [email protected]
More: Value stocks are poised to crush growth stocks after the presidential election






