(Bloomberg Opinion) — “Uber, but for short-term restaurant and warehouse jobs,” sounds like a startup pitch circa 2015. But the actual Uber Technologies Inc. is expanding a test of a temporary staffing program.
I’ve been skeptical of Uber and other logistics companies that say they can capably match supply and demand for a host of goods and services. But this could work. Uber’s network has several million drivers, some of whom might be interested in picking up other flexible work. With U.S. unemployment at low levels, many businesses are eager to find good workers, too.
The staffing story also reminded me how quickly the balance has shifted from Uber’s promise to its reality. Before Uber’s IPO flopped in May, there was more patience for experiments to get bigger and broader. Now, apart from this relatively low-stakes staffing project, the pressure is on for the company to focus on what works right now.
Facing investor doubts and a 33% share decline from its IPO, Uber recently pledged to deliver adjusted profits much more quickly than anyone had expected. Uber is on the clock to prioritize its most promising businesses and markets and abandon many projects that can’t pay for themselves relatively quickly. You can see can that in Uber’s cost-cutting, continuing discussions to sell its food-delivery business in India, and its discontinued restaurant-kitchen rental pilot project.
Uber has backed away before from cash-burning businesses with uncertain payoff. There is more urgency now for the company to change the balance between the future and the now.
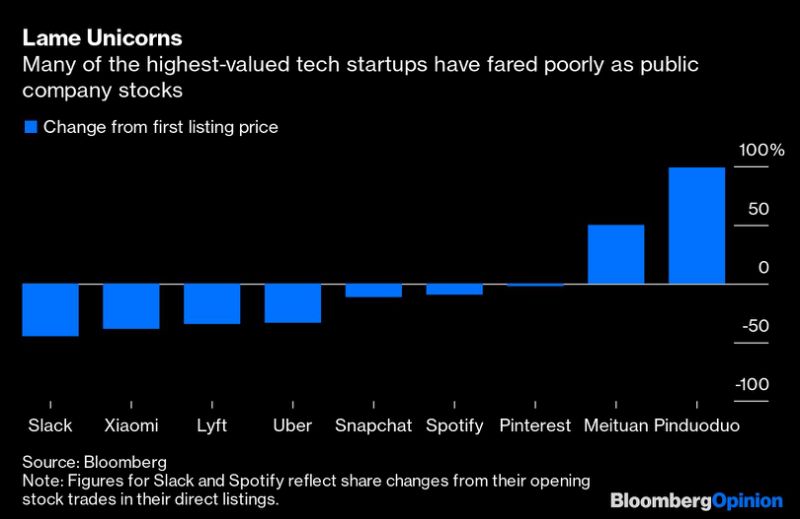
Other companies will or are confronting this shift. Post-IPO share declines of Uber, Lyft Inc., Snap Inc., Pinterest Inc. and other richly valued former startups reflect in part investor skittishness about funding fast-growing but sometimes cash-hungry businesses. More young companies will be judged by what they are doing rather than what they might be able to accomplish in a starry future.(1) It’s no longer viable to count on expanding in perpetuity with other people’s money.
The sudden impatience about startups has also trained a spotlight on the SoftBank Vision Fund, the $100 billion investment pool that is all about encouraging short-term losses to fulfill outsize promise. If you haven’t already, it’s essential to read this Bloomberg Businessweek article about how the Vision Fund operates.
Its strategy of arming startups with bazookas of cash means they must think incredibly big to generate bazooka-like returns. That creates sometimes perverse incentives. In one episode, SoftBank’s powerful leader yelled at an underling for steady but slow progress at a portfolio company. A SoftBank-backed automated pizza startup was urged to chase a reorientation of the U.S. food production system. (“Are we the next Theranos?” as one Zume Pizza Inc. worker asked in a management Q&A, is probably not something Domino’s Pizza bosses have to tackle.)
The struggles of SoftBank-backed Uber and WeWork are justifiably calling attention to the downsides of motives to grab for the the biggest potential outcome at any cost. WeWork wasn’t “elevating the world’s consciousness.” It was a real estate arbitrage company burning piles of SoftBank’s money to find growth with little oversight because no one had an incentive to confront the warning signs.
WeWork is the worst-case scenario. But it’s also true that the abundance of capital available to certain kinds of superstar companies in the last decade has enabled some very big and handy ideas.
Uber and similar services couldn’t exist in their current forms without mountains of capital. Cash-burning Netflix Inc. couldn’t exist without people willing to bankroll a globe-spanning digital television network.
The last decade’s bazookas of cash brought many good ideas to life. Bad news: They might not be financially viable when those bazookas run out of ammo. And it also means there are rich motivations for outlandish ideas pursued with recklessness.
A version of this column originally appeared in Bloomberg’s Fully Charged technology newsletter. You can sign up here.
(1) The changing distaste for short-term losses can affect public companies. Share Now, an urban car-rental project backed by automakers BMW AG and Daimler AG, said Wednesday that it wouldend operations in North America and three European cities.
To contact the author of this story: Shira Ovide at [email protected]
To contact the editor responsible for this story: Daniel Niemi at [email protected]
This column does not necessarily reflect the opinion of the editorial board or Bloomberg LP and its owners.
Shira Ovide is a Bloomberg Opinion columnist covering technology. She previously was a reporter for the Wall Street Journal.
<p class="canvas-atom canvas-text Mb(1.0em) Mb(0)–sm Mt(0.8em)–sm" type="text" content="For more articles like this, please visit us at bloomberg.com/opinion” data-reactid=”40″>For more articles like this, please visit us at bloomberg.com/opinion
©2019 Bloomberg L.P.