-
Institutions’ substantial holdings in Amazon.com implies that they have significant influence over the company’s share price
-
A total of 25 investors have a majority stake in the company with 47% ownership
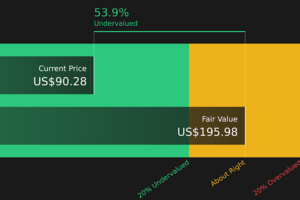
A look at the shareholders of Amazon.com, Inc. (NASDAQ:AMZN) can tell us which group is most powerful. We can see that institutions own the lion’s share in the company with 63% ownership. Put another way, the group faces the maximum upside potential (or downside risk).
Given the vast amount of money and research capacities at their disposal, institutional ownership tends to carry a lot of weight, especially with individual investors. Hence, having a considerable amount of institutional money invested in a company is often regarded as a desirable trait.
Let’s delve deeper into each type of owner of Amazon.com, beginning with the chart below.
Check out our latest analysis for Amazon.com
Many institutions measure their performance against an index that approximates the local market. So they usually pay more attention to companies that are included in major indices.
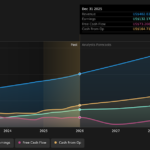
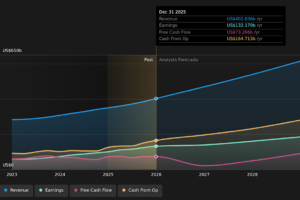
Amazon.com already has institutions on the share registry. Indeed, they own a respectable stake in the company. This suggests some credibility amongst professional investors. But we can’t rely on that fact alone since institutions make bad investments sometimes, just like everyone does. When multiple institutions own a stock, there’s always a risk that they are in a ‘crowded trade’. When such a trade goes wrong, multiple parties may compete to sell stock fast. This risk is higher in a company without a history of growth. You can see Amazon.com’s historic earnings and revenue below, but keep in mind there’s always more to the story.
Investors should note that institutions actually own more than half the company, so they can collectively wield significant power. Amazon.com is not owned by hedge funds. Our data suggests that Jeffrey Bezos, who is also the company’s Top Key Executive, holds the most number of shares at 8.7%. When an insider holds a sizeable amount of a company’s stock, investors consider it as a positive sign because it suggests that insiders are willing to have their wealth tied up in the future of the company. In comparison, the second and third largest shareholders hold about 7.7% and 6.2% of the stock.
Our studies suggest that the top 25 shareholders collectively control less than half of the company’s shares, meaning that the company’s shares are widely disseminated and there is no dominant shareholder.
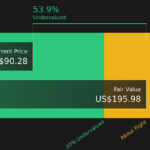
Researching institutional ownership is a good way to gauge and filter a stock’s expected performance. The same can be achieved by studying analyst sentiments. There are plenty of analysts covering the stock, so it might be worth seeing what they are forecasting, too.
The definition of an insider can differ slightly between different countries, but members of the board of directors always count. The company management answer to the board and the latter should represent the interests of shareholders. Notably, sometimes top-level managers are on the board themselves.
I generally consider insider ownership to be a good thing. However, on some occasions it makes it more difficult for other shareholders to hold the board accountable for decisions.
Our information suggests that insiders maintain a significant holding in Amazon.com, Inc.. Insiders own US$223b worth of shares in the US$2.1t company. That’s quite meaningful. It is good to see this level of investment. You can check here to see if those insiders have been buying recently.
The general public– including retail investors — own 26% stake in the company, and hence can’t easily be ignored. While this group can’t necessarily call the shots, it can certainly have a real influence on how the company is run.
While it is well worth considering the different groups that own a company, there are other factors that are even more important.
Many find it useful to take an in depth look at how a company has performed in the past. You can access this detailed graph of past earnings, revenue and cash flow.
Ultimately the future is most important. You can access this free report on analyst forecasts for the company.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.